Predictive analysis of the Russia - Ukraine conflict - AI Assessment
Predictive analysis of the Russia - Ukraine conflict | B | G
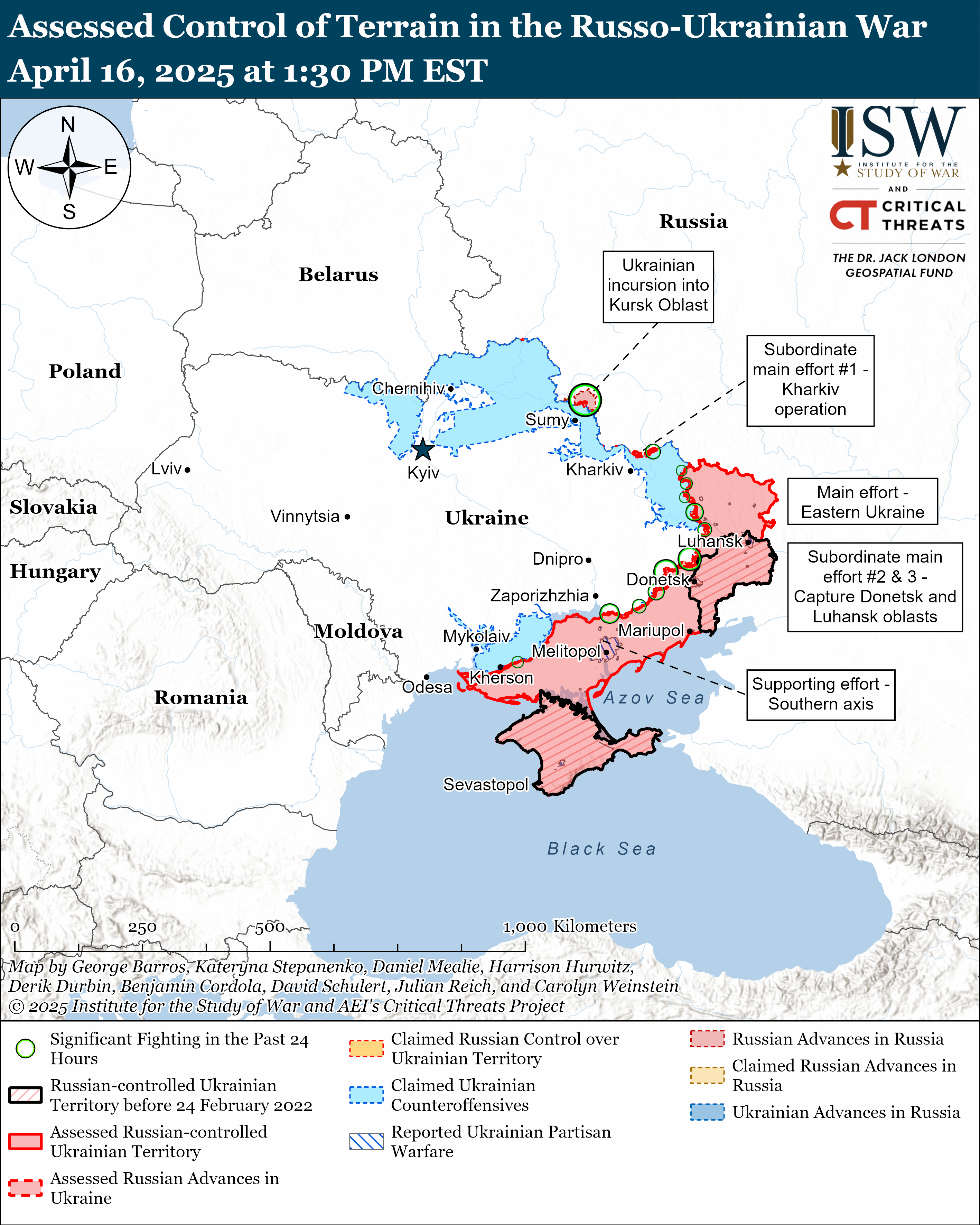
Russia - Ukraine War
Predictive analysis of the RussiaUkraine conflict focuses on using data and models to anticipate potential outcomes, including the likelihood of escalation, the impact on global grain security, and even the future of military logistics. This analysis helps understand the complex dynamics of the conflict and potentially guide decision-making for conflict prevention and response. [1, 2, 3, 4]
- AI and machine learning models: These models can analyze various data points, such as social media trends, news articles, and military deployments, to identify patterns and predict potential escalations or shifts in the conflict. [4, 4, 5, 5, 6, 7]
- Early warning tools: These tools, ranging from qualitative data analysis to advanced AI, are used to anticipate the impacts of conflict and violence, including the potential for escalation. [3, 3, 4, 4]
- Geospatial analysis: Analyzing the spatial distribution of events, such as air alerts, can help predict where and when conflicts might occur. [7, 7, 8, 8]
- Predictive peacebuilding: This approach uses data science to understand the roots and warning signs of conflict, aiming to develop strategies for preventing and mitigating conflict. [3, 3]
- Global grain security: Predictive models can assess the impact of the conflict on global food prices and grain security, helping to anticipate potential shortages and resource allocation. [2, 2, 9]
- Economic impacts: Analysis can predict the economic consequences of the conflict, including impacts on trade, investment, and energy markets. [2, 10, 10, 11, 12]
- Military logistics: Predictive analytics can help optimize supply chains and resource allocation for military operations, potentially reducing vulnerabilities and improving efficiency. [1, 1, 13]
- AI-enabled warfare: The conflict highlights the increasing role of AI in military operations, including intelligence analysis, drone control, and electronic warfare. [5, 5, 14, 14, 15, 15]
- Cybersecurity implications: The conflict has raised concerns about the use of AI for cybersecurity and the need to strengthen data encryption and exchange networks. [5, 5]
- Digital transformation: The conflict has accelerated the shift towards cloud computing and digital infrastructure in both military and civilian sectors. [16, 16, 17]
- Unpredictability of human behavior: Predicting the actions and intentions of actors in a conflict is inherently complex and can be challenging for models to capture. [7, 18]
- Data limitations: The availability and quality of data can affect the accuracy and reliability of predictive models. [19, 19, 20]
- Evolving nature of conflict: The conflict is constantly evolving, and models may need to be updated and recalibrated to stay relevant. [8, 8, 21, 22, 23]
- Military Dynamics:
- Russia's Strategy and Resources: Russia has adopted a strategy of attritional warfare, aiming to exhaust Ukraine through sustained pressure and incremental territorial gains. In 2024, Russian forces gained approximately 4,168 km², primarily in Donetsk, but at a high cost, with reported casualties exceeding 420,000 for the year. Russia's tank reserves are dwindling, with estimates suggesting stocks of restorable tanks may be exhausted by mid-2025, and restoration rates have dropped significantly. Artillery and rocket launcher shortages could emerge by 2025-2026. Manpower remains a challenge, with recruitment struggling to keep pace with losses (40,000 recruits vs. 40,000 losses monthly in early 2025).
- Ukraine's Capabilities: Ukraine has demonstrated resilience, inflicting unsustainable losses on Russian forces while holding key defensive lines. Ukrainian drone warfare has improved, with FPV drones destroying 85% of Russian targets in the Pokrovsk direction by early 2025, up from 50% in mid-2024. However, Ukraine faces manpower shortages, exacerbated by reluctance to mobilize 18- to 25-year-olds, and relies heavily on Western aid for artillery, air defense (e.g., Patriot systems), and long-range systems (HIMARS, ATACMS).
- Western Support: The suspension of U.S. military aid and intelligence sharing in March 2025 has strained Ukraine’s capabilities, with Patriot missile stocks potentially depleting by mid-2025. Europe has increased support, with Germany, France, the Netherlands, and the UK committing billions in aid and drone production, but it may not fully offset U.S. reductions. European defense production is ramping up, potentially meeting more of Ukraine’s needs by late 2025.
- Economic and Domestic Factors:
- Russia: Russia’s economy faces stagflation risks, with inflation at 10.2% in early 2025 and projected to fall to 7-8% by year-end. Military spending (6% of GDP) sustains the war effort, but sanctions and equipment losses limit long-term capacity. Public support for negotiations is around 60%, but Putin’s insistence on maximalist goals (regime change, territorial concessions) limits diplomatic flexibility.
- Ukraine: Ukraine’s economy shows resilience, with projected GDP growth of 2.5-3.5% in 2025, supported by domestic defense production (up from 1.3 billion to 20 billion hryvnia, 2014-2024) and EU investments. However, energy infrastructure attacks and population displacement (7 million refugees) strain recovery. The IMF’s baseline scenario assumes the war ends by late 2025, but a prolonged conflict could deepen fiscal deficits.
- Geopolitical and Diplomatic Context:
- U.S. Policy under Trump: The Trump administration’s push for a ceasefire, coupled with aid pauses, pressures Ukraine to negotiate. Trump’s unpredictability complicates predictions, but his focus on forcing negotiations may lead to concessions that favor Russia unless Putin overplays his hand.
- Russia’s Stance: Putin has rejected ceasefire proposals unless they include Ukrainian capitulation, demilitarization, and territorial losses. Kremlin narratives portray Ukraine as an illegitimate negotiating partner, aiming to undermine Western support.
- Allied Support: NATO and EU countries remain committed, with increased defense budgets and production (e.g., Rheinmetall’s nitrocellulose expansion for artillery shells). However, political fatigue in the West and competing global crises (e.g., Middle East, Taiwan) could dilute focus on Ukraine.
- Third-Party Actors: Russia relies on North Korean troops (withdrawn in February 2025 after high casualties) and Iranian drones, while China provides indirect support via sanctions evasion. These partnerships bolster Russia but are insufficient to decisively shift the balance.
- Technological and Tactical Innovations:
- Drones and Motorcycles: Both sides are adapting. Russia is developing motorcycle-based tactics for speed and maneuverability to evade drones, while Ukraine’s drone production and integration with ground operations are advancing.
- Energy Infrastructure Attacks: Russia’s targeting of Ukraine’s energy grid aims to cripple its economy and morale, while Ukraine’s drone strikes on Russian oil facilities (6,500+ in 2024) disrupt Moscow’s revenue.
- AI and Electronic Warfare: AI-guided munitions and electronic warfare are increasingly critical, with Ukraine testing new prototypes to counter Russian advances.
- Ceasefire Agreement (60% Likelihood):
- Description: A fragile ceasefire is negotiated, likely under U.S. pressure, freezing the front line without resolving territorial disputes. Both sides maximize territorial gains before talks, with Russia holding ~20% of Ukraine and Ukraine retaining parts of Kursk. Terms may include prisoner swaps (as seen in April 2025), bans on energy infrastructure strikes, and Black Sea truces.
- Drivers: Trump’s threat to cut aid forces Zelensky to negotiate, while Putin faces domestic pressure (60% of Russians support talks) and equipment shortages. European aid sustains Ukraine’s leverage, preventing total capitulation.
- Implications: A ceasefire allows Ukraine to lift martial law, hold elections, and begin reconstruction, but violations are likely, as seen post-Minsk Agreements. Russia may use the pause to rebuild forces, while Ukraine strengthens its defense industry. Global energy markets stabilize, but geopolitical tensions persist.
- Protracted Attritional Conflict (35% Likelihood):
- Description: The war continues as a stalemate, with neither side achieving a breakthrough. Russia makes marginal gains (e.g., in Donetsk, Luhansk) but lacks resources for decisive victories. Ukraine holds defensive lines but struggles with manpower and U.S. aid cuts. Trench warfare and drone-heavy tactics dominate, with high casualties on both sides.
- Drivers: Putin rejects ceasefire terms if Russia captures key logistical hubs (e.g., Pokrovsk), believing military victory is achievable. Ukraine’s resilience, bolstered by European aid and domestic production, prevents collapse. Western fatigue and U.S. isolationism limit support, prolonging the stalemate.
- Implications: Ukraine’s economy faces deeper shocks, with inflation rising and reconstruction delayed. Russia’s economy stagnates further, risking social unrest. Global attention shifts to other conflicts, reducing diplomatic pressure for resolution.
- Decisive Shift (5% Likelihood):
- Description: Either side achieves a significant breakthrough, leading to a Ukrainian victory (retaking pre-2022 borders) or Russian victory (major territorial gains, regime change). A Ukrainian collapse is less likely due to European support, while a Russian collapse could stem from economic implosion or internal dissent.
- Drivers: For Ukraine, a surge in Western aid (e.g., lifted restrictions on long-range strikes) or Russian overextension could enable a counteroffensive. For Russia, a complete U.S. aid cutoff and Ukrainian manpower shortages could tip the balance. A sudden leadership change (e.g., Putin’s removal) could also disrupt Russia’s war effort.
- Implications: A Ukrainian victory would bolster NATO and European security but strain Russia’s global influence. A Russian victory would embolden authoritarian regimes and destabilize Europe, impacting global trade and security.
- U.S. Policy Consistency: Trump’s unpredictability could lead to renewed aid or further cuts, dramatically affecting Ukraine’s resilience.
- Russian Domestic Stability: Economic strain and casualty backlash could force Putin to negotiate or escalate, depending on internal pressures.
- European Commitment: If Europe fully compensates for U.S. aid reductions, Ukraine’s defensive capacity strengthens; otherwise, vulnerabilities grow.
- Technological Edge: Advances in drones, AI, or electronic warfare could shift tactical advantages, though neither side currently holds a decisive edge.
https://t.co/HWmiUnWh7k
— Michael Novakhov (@mikenov) April 27, 2025
AI Report#NewsAndTimes #NT #TNT #News #Times #World #USA #POTUS #DOJ #FBI #CIA #DIA #DOD #ODNI #Trump #TrumpNews #TRUMPISTAN #Israel #Mossad #Netanyahu #Ukraine #NewAbwehr #OSINT #Putin #Russia #GRU #Путин #Россия #Bloggers #Opinions #SouthCaucasus
-… https://t.co/DF6wgwVtvY pic.twitter.com/uiQwnDlF5Y


Comments
Post a Comment